Here you can find the different sections of the interactive map:
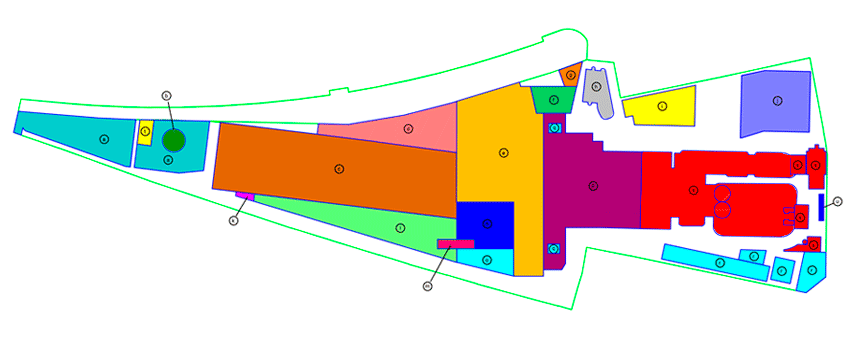
A – BIOMETHANISATION
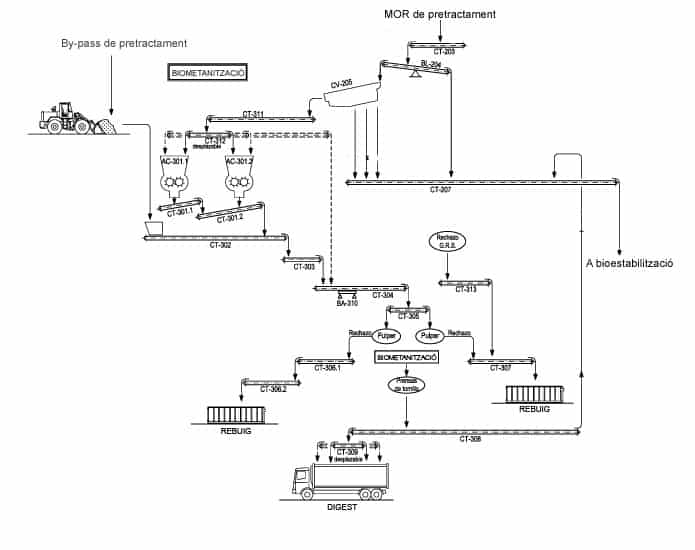
The organic fraction part that is not destined to the composting or aerobic stabilization area reaches this area to be treated anaerobically, that is, in absence of oxygen.
After a first separation of improper material waste in dry, the organic matter undergoes an advanced wet pretreatment that allows the clean organic suspension to reach the 2 digestors in optimal conditions for the generation of biogas thanks to the complex biological activity of the anaerobic microorganisms.
The biogas generated is sent to 2 combustion engines that produce electricity, nearly 13 million kWh/year, and heat that is used to heat the digestors and for the hygienisation of the digest –suspension coming out from the digestors–.
The production of electricity makes it possible to prevent the emission of more than 5,000 tons CO2/year to the atmosphere, which is equivalent to planting around 250,000 trees, or a forest covering the same surface as the town of Canet de Mar (625 Ha).
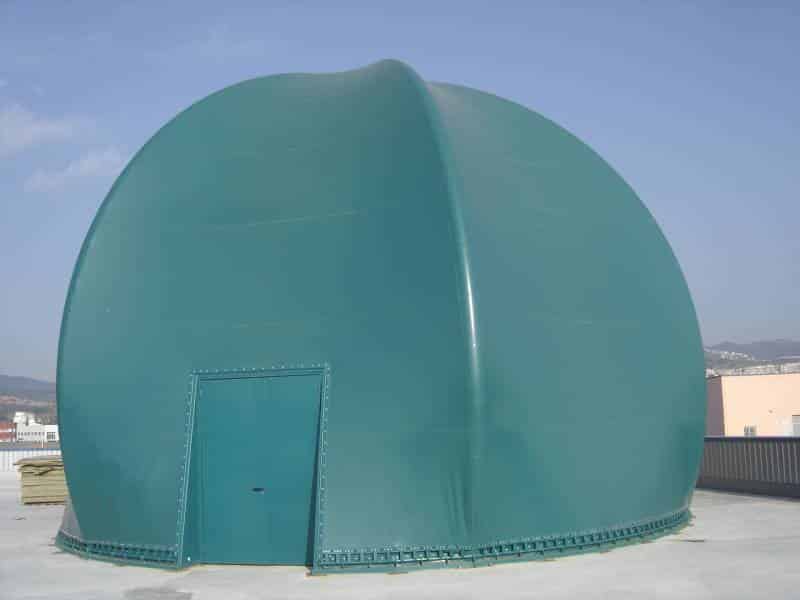

B - GREEN SPHERE
It is a space for reflection, which aims to be a demonstration point that another reality is possible and that is taking place: the Circular Economy.
The linear system of the current economy (extraction of materials, manufacturing, use and disposal of waste) has been exhausted, as there are a number of natural resources and fossil fuels in the phase of disappearing.
The Green Sphere aims to explain in a very simple and didactic way the concept of the Circular Economy: using waste as resources to achieve an efficient cycle of materials and intelligent, sustainable and inclusive growth.
Principles of Circular Economy:
– Initial eco-design considering the environmental impacts throughout the life cycle of the product due to its integration.
– Optimized management of stocks and flows of materials, energy and services of industrial organizations.
– Prioritize functionality, the sale of a service in front of a material asset.
– Reuse of goods or products for reuse after their useful life, in the same function or in another, directly or after a restoration or reconditioning action.
– Repair to find a second life to products without service.
– Recycling to take advantage of the materials found in the waste.
– Energy recovery of waste that cannot be recycled.
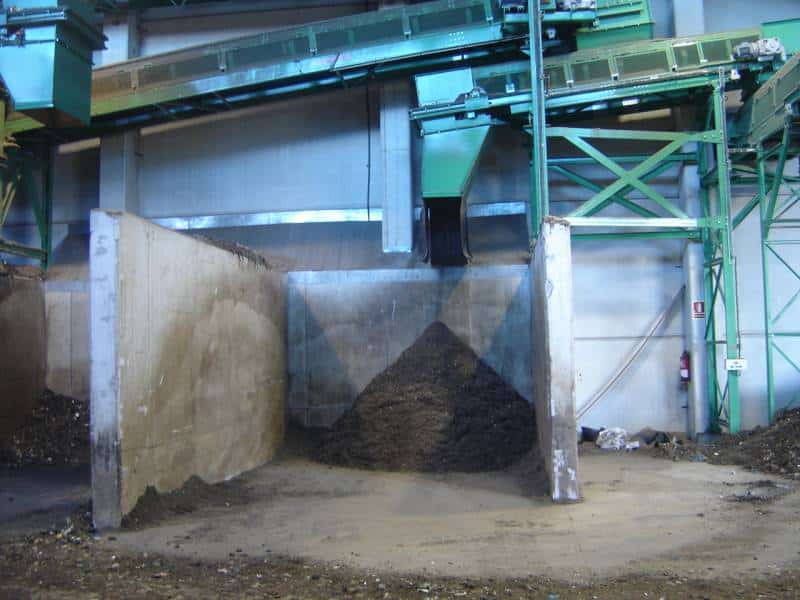
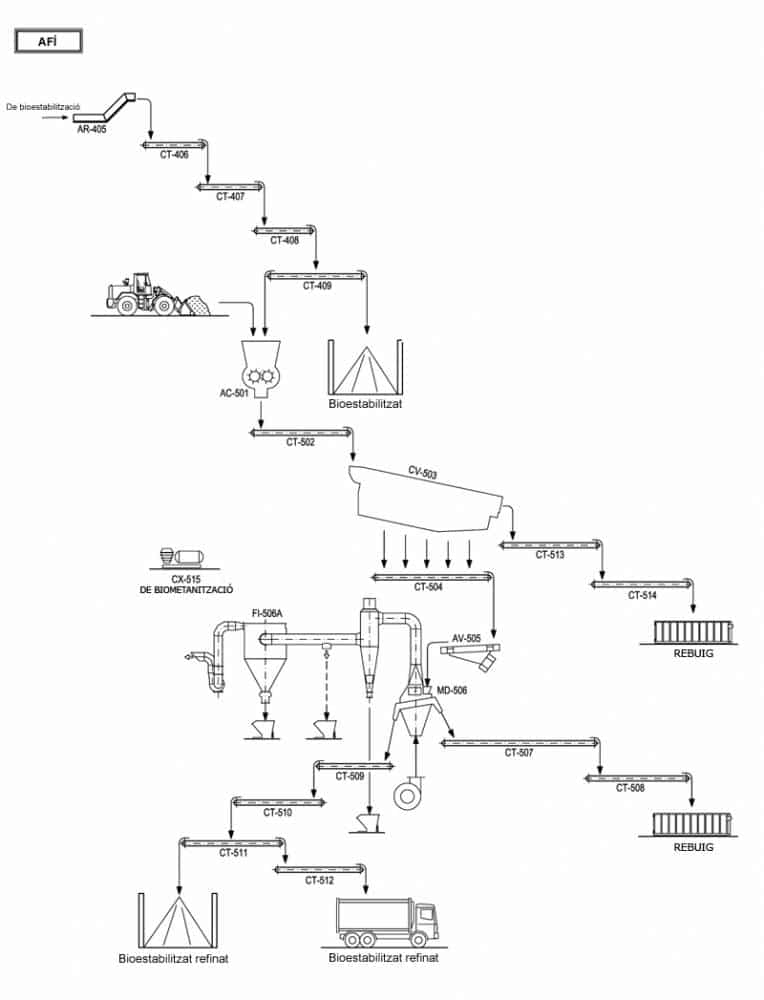
C - BIOSTABILISATION
In the facilities, the organic fraction is treated thanks to the biological activity of the aerobic microorganisms present in the organic matter.
Here comes a part of the organic fraction separated in the pretreatment and the digest generated in the methanization or anaerobic digestion area.
To make the activity of microorganisms useful, the level of humidity and the temperature need to be controled, and there has to be some ventilation. This way, the biological process is enhanced.
D - AIR TREATMENT
The air and odour treatment system is key to the good operation of the Centre. It is integrated by a high-tech inorganic biofilter and an RTO or Regenerative Thermal Oxidation.
All this, together with the air used in the Waste-to-Energy plant for combustion process, offers a total capacity 400,000 m3/h for the treatment of odours.
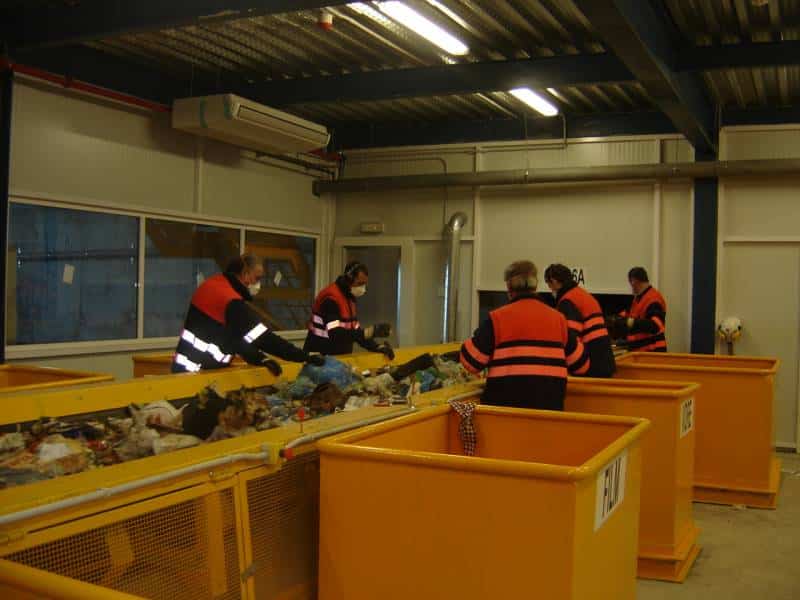
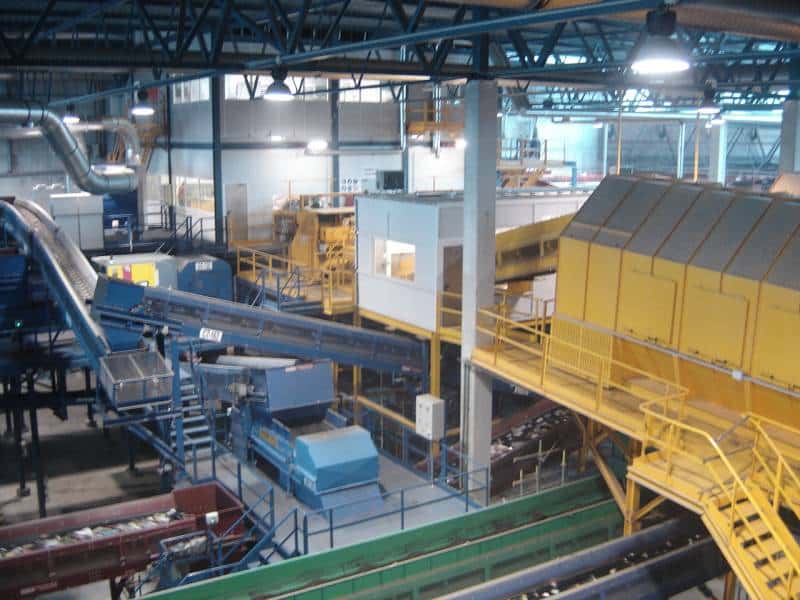
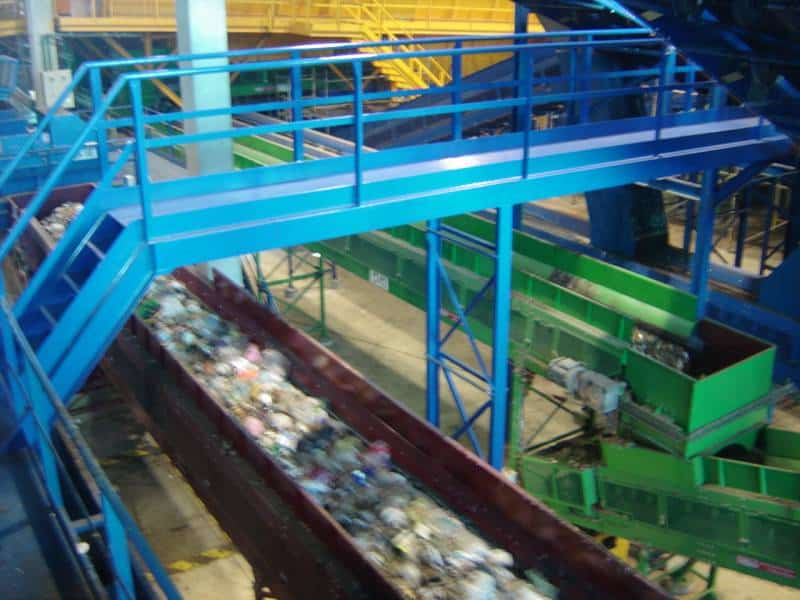
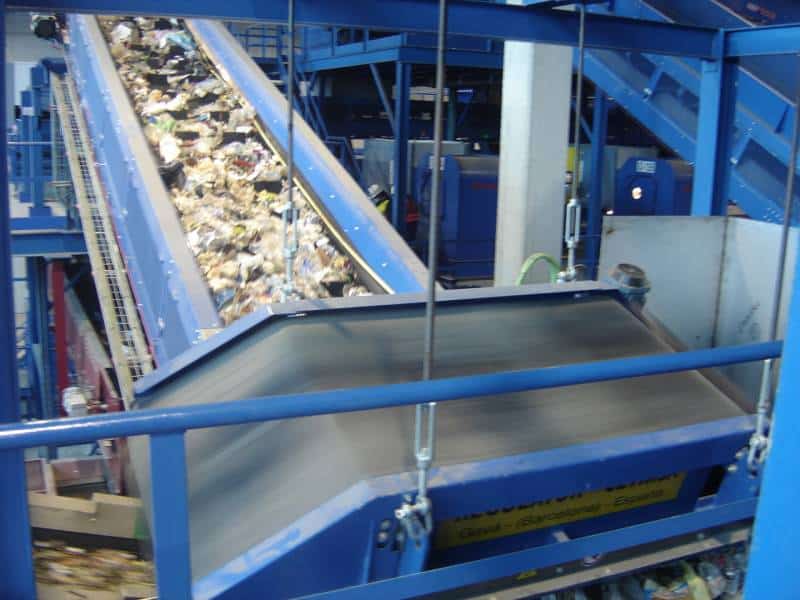
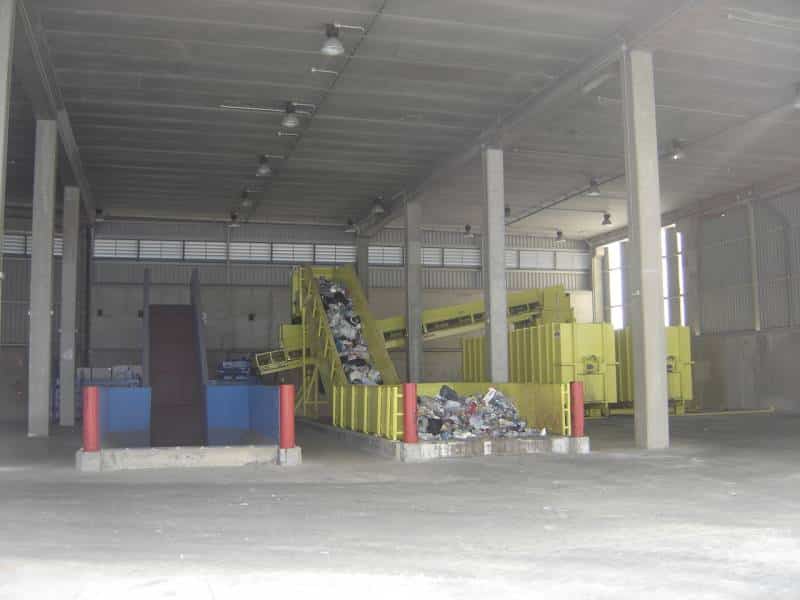
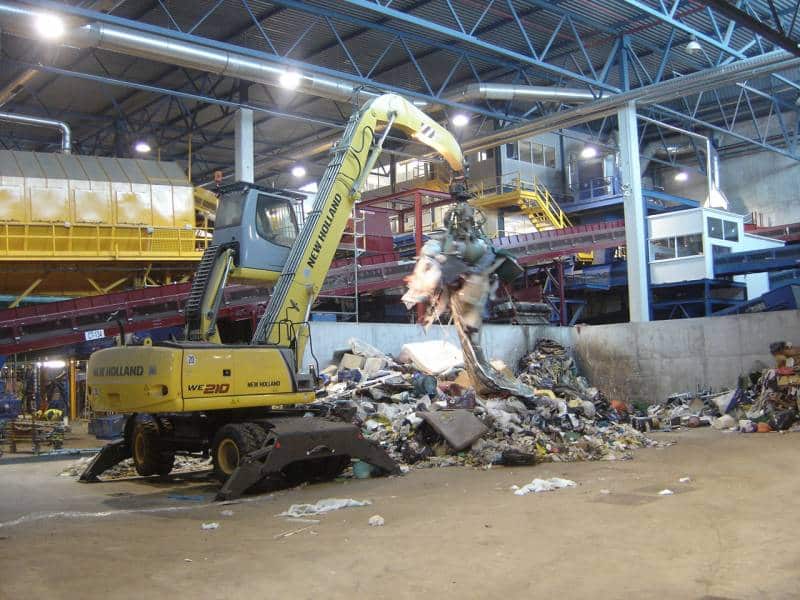
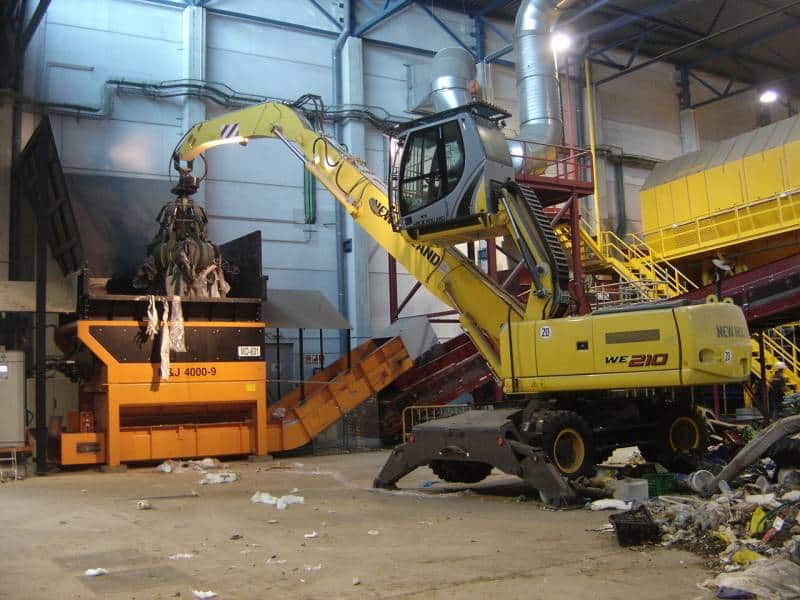
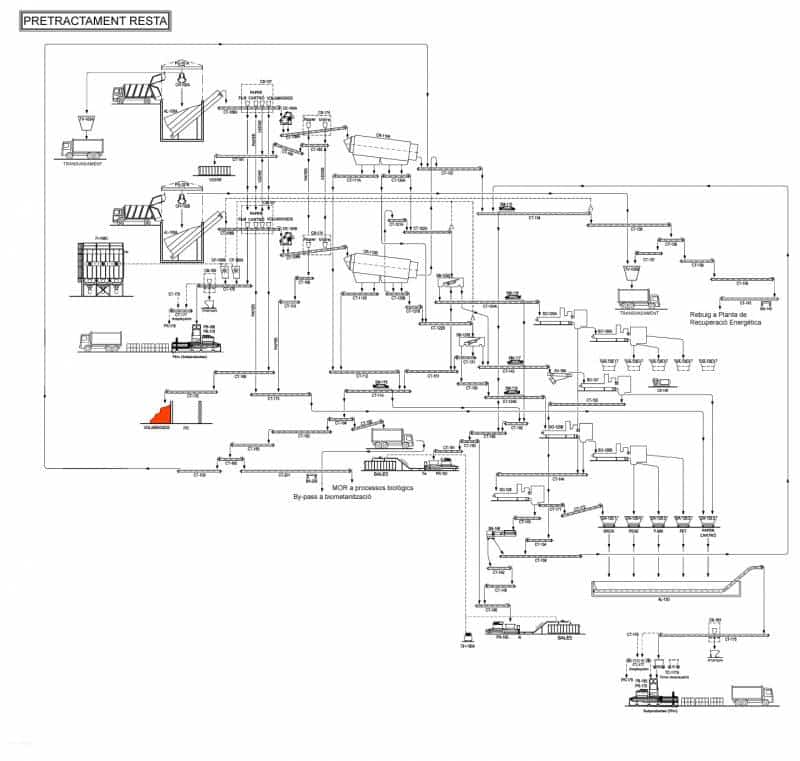
E - PRE-TREATMENT
Here, waste is separated according to its size, geometry and composition. An amount of 16,000 tons a year of recyclable materials is obtained.
Several advanced automatic systems play a part in this task: bag openers, trommels, ballistic separators, optic separators, magnetic separators, Foucault separators, film aspirations, presses, etc., combined with manual sorting at strategic points of the process.
The separated organic matter is sent to the biological processes, while the combustible waste is converted into heat and electricity.
You can follow the journey of the main fractions according to the color coding:
Yellow: Initial feeding and separation systems
Green: Small or organic fraction (0-70 mm)
Blue: Medium or light packaging fraction (70-200 mm)
Red: Big or combustible waste fraction (> 200 mm)
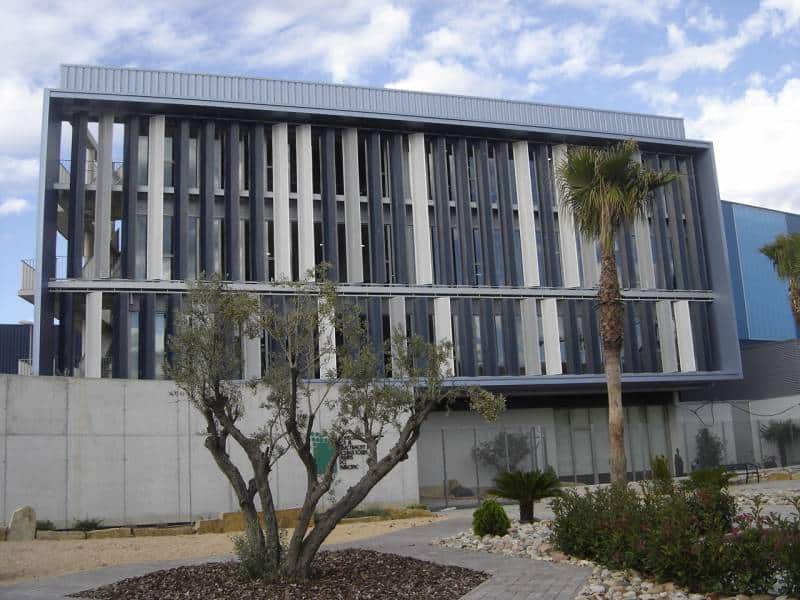
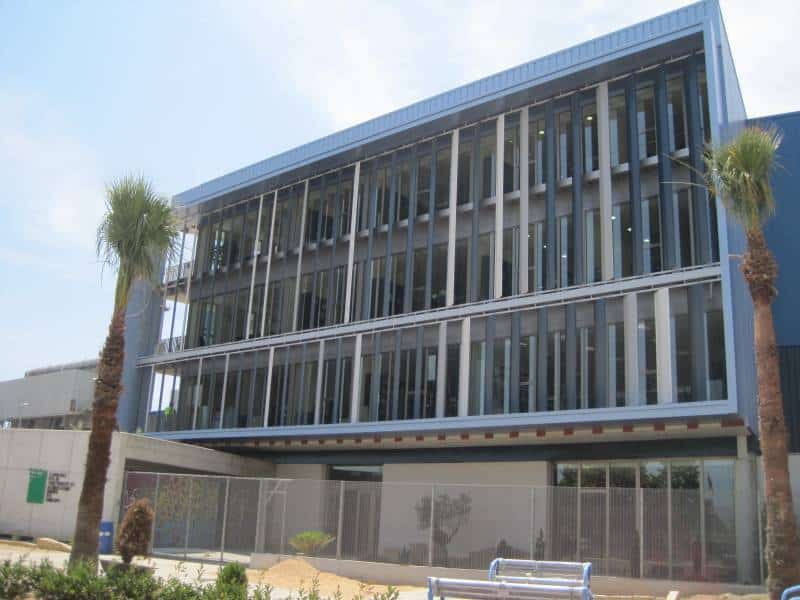
F - ADMINISTRATIVE BUILDING
Access to the Centre Integral de Valorització de Residus del Maresme is through the main entrance of the administrative building, located at Carrer de la Teixidora, 83, 08302 Mataró.
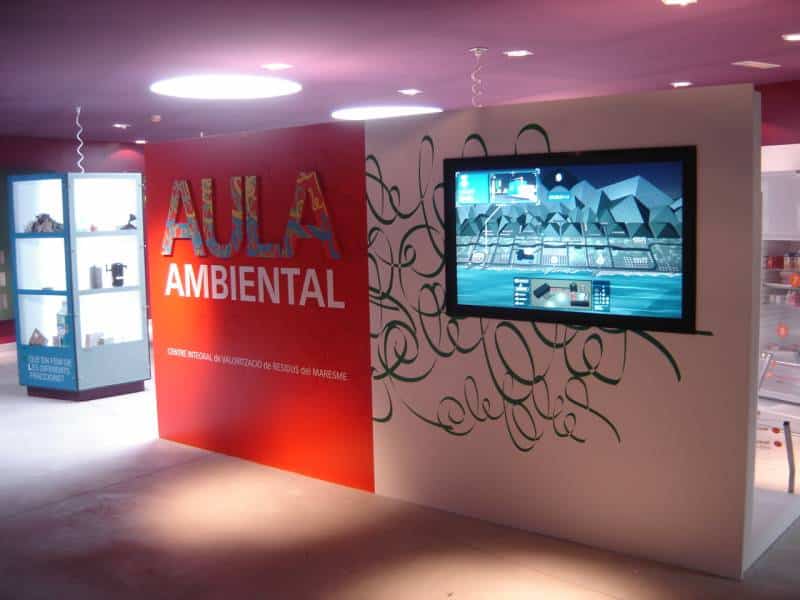
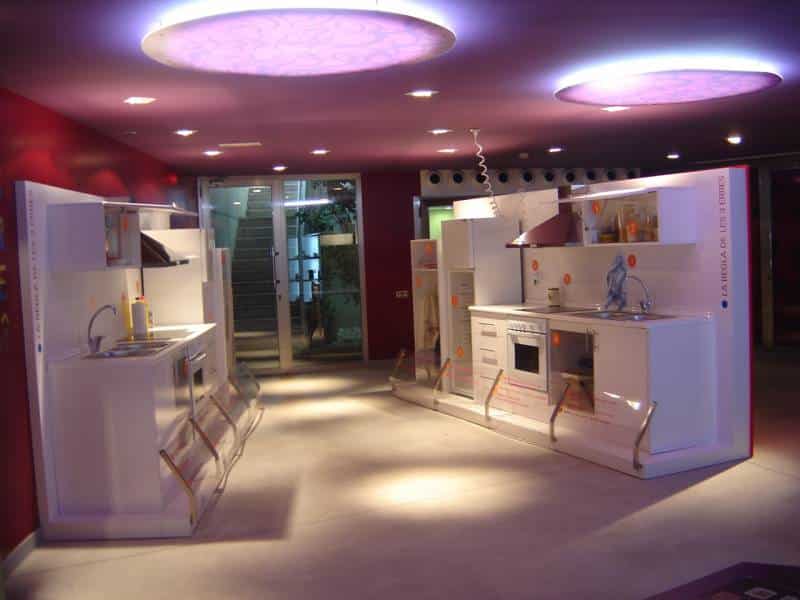
G - ENVIRONMENTAL CLASSROOM
This covers three scope areas:
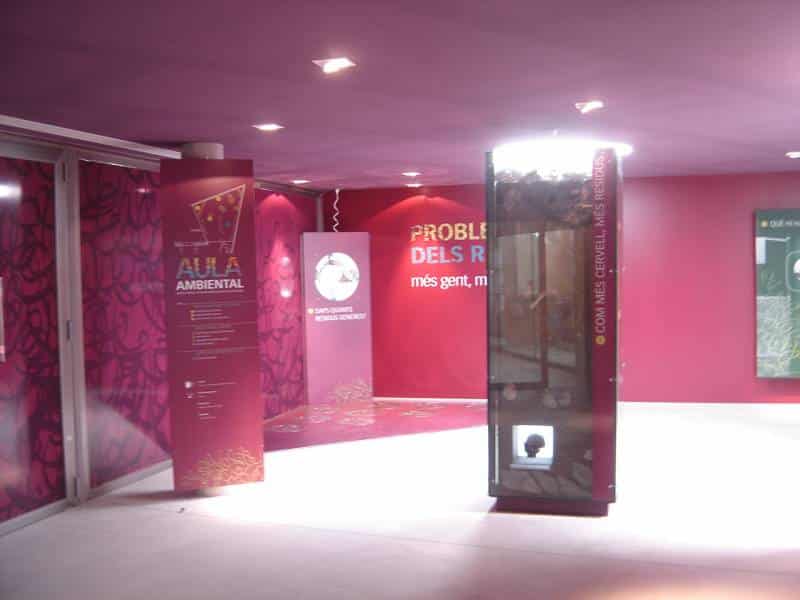
Scope area A: Section dividided into three modules where problems posed by waste to society are shown. The modules are:
– Module 1: The bigger the brain, the more the waste?
– Module 2: Do you know how much waste you generate?
– Module 3: What is there behind what you consume?
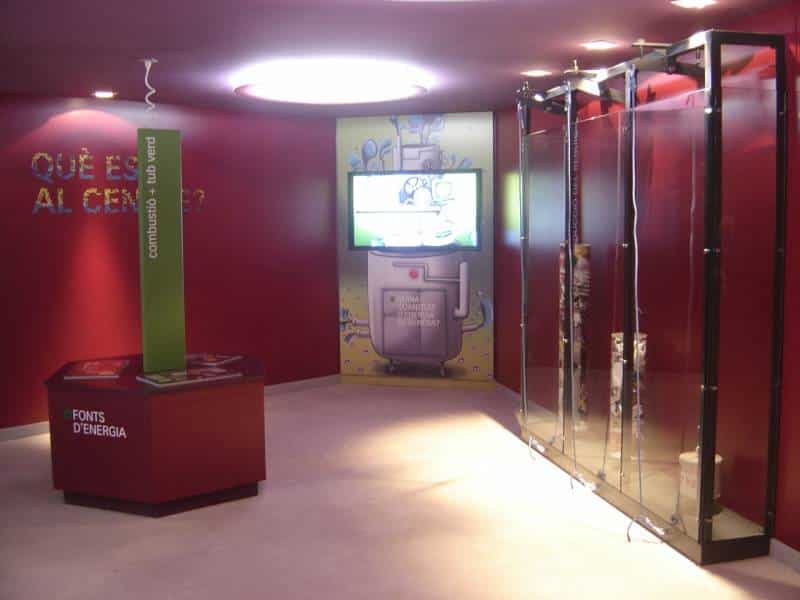
Scope area B: Section divided into four modules where what is done with the waste in the Centre is shown. The modules are:
– Module 4: Types of waste, separation and reuse
– Module 5: Energy sources
– Module 6: How much energy is generated?
– Module 7: Reduction of refuse
Scope area C: Section with one module only where what can be done at home to minimize waste is shown.
– Module 8: The rule of the “Three Rs”
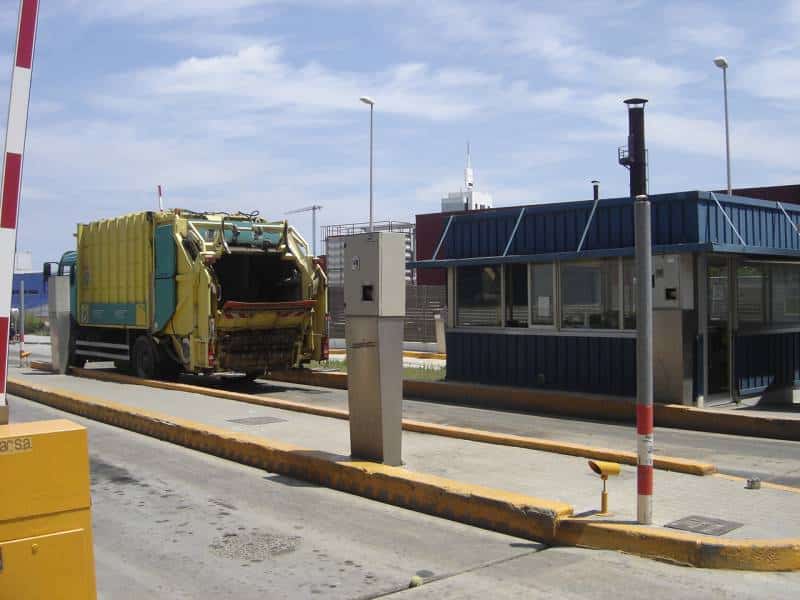
H - ACCESS CONTROL AND SCALES
At the entrance of the facilities there are weighing scales where all the arriving trucks are weighed both on their way in and on their way out. All the necessary details are also collected to have control of all the trucks going into the Centre. After weighing, the trucks go to the reception hall.
I - WAREHOUSE, CHANGING ROOMS AND LAVATORIES
There is a new area with toilets and changing rooms for the workers, in addition to the new warehouse.
Changing rooms and warehouse building

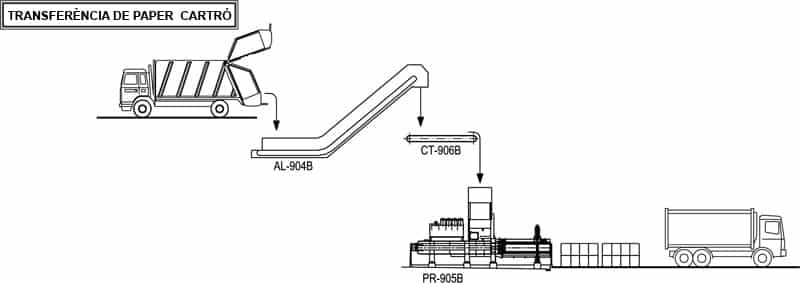
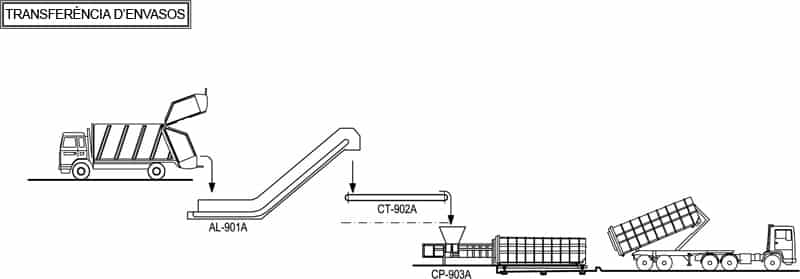
J - TRANSFER OF LIGHT PACKAGING AND PAPER AND CARDBOARD
This consists in unloading and feeding to the final recuperators the paper and cardboard and light packaging coming from the separate collection.
In the case of paper/carboard, compressed bales are made in order to optimize transport, while in the case of packages, compacting containers are used to transport the waste to the packaging selection plant.
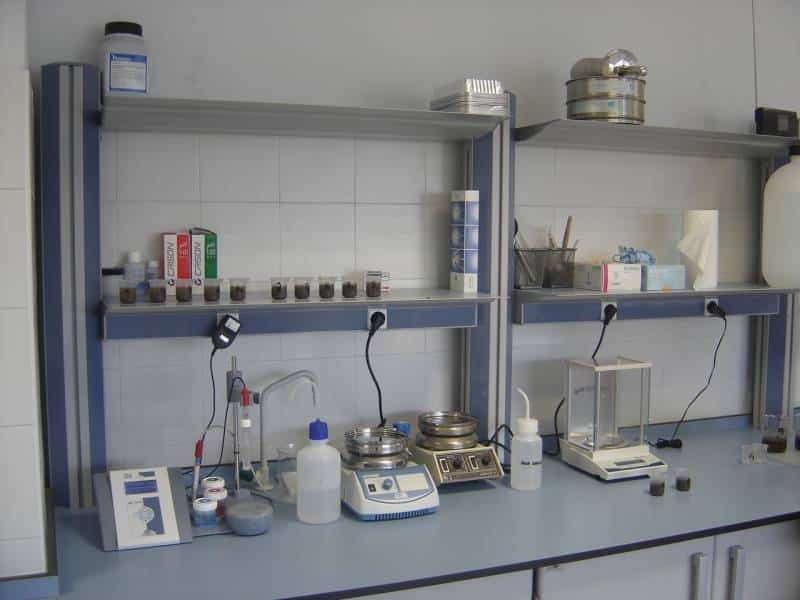
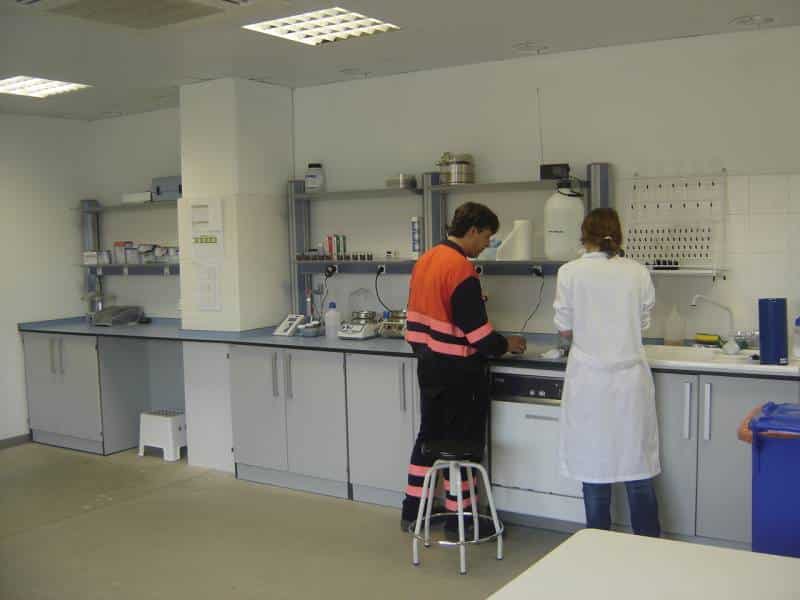
K - LABORATORY
Here, solid and liquid materials at different stages of the process are analyzed. Specifically, humidity, pH, conductivity, stability of the product, and other variables are analyzed.
L - REFINEMENT
Stabilized organic matter from the composting or aerobic stabilization stage arrives here. This material, once stabilized and matured, still contains a significant amount of inert and improper materials which need to be separated in order to obtain a final product of the greatest possible quality.
To achieve this, the stabilized product goes through a vibrating sieve and a densimetric table which ensures the product is apt for its end use.
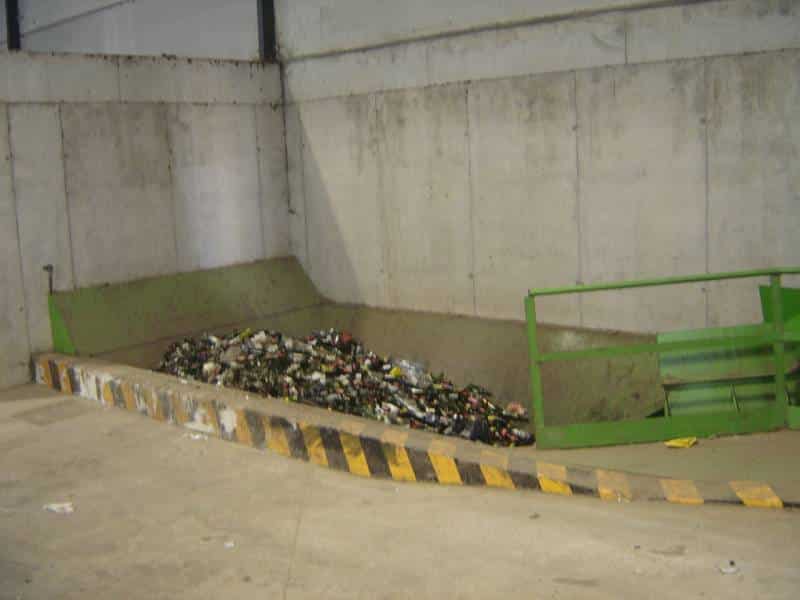
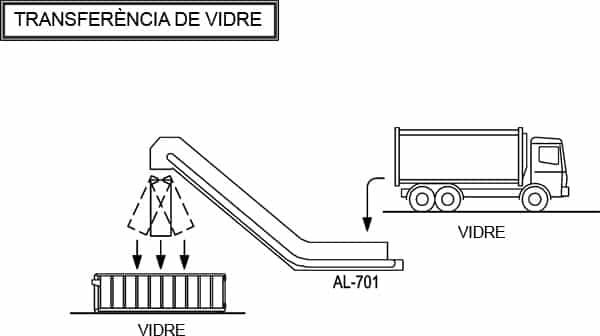
M - TRANSFER OF GLASS
This is the unloading and automatic feeding from the separate collection area where glass is transferred to the final recuperators. In order to optimize its transportation, glass is collected in containers and is moved in heavier duty trucks.
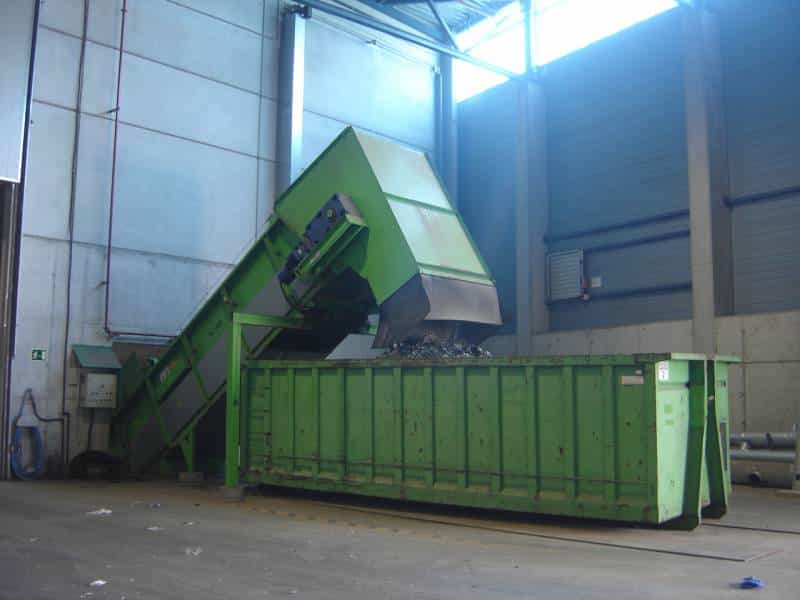
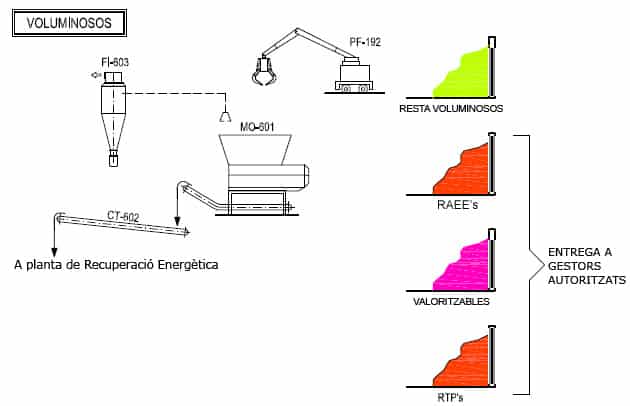
N - BULKY WASTE PLANT
We are in front of the processing area of the socalled bulky waste (furniture, old pieces of junk, matresses, big pieces of wood, and the like). This is the destination of both this kind of waste separated at the beginning stage of the pretreatment and the specific loads of trucks destined to this type of collection.
The objective is to manually sort all the recyclable materials and shred the rest to send it to the Waste-to-Energy plant.
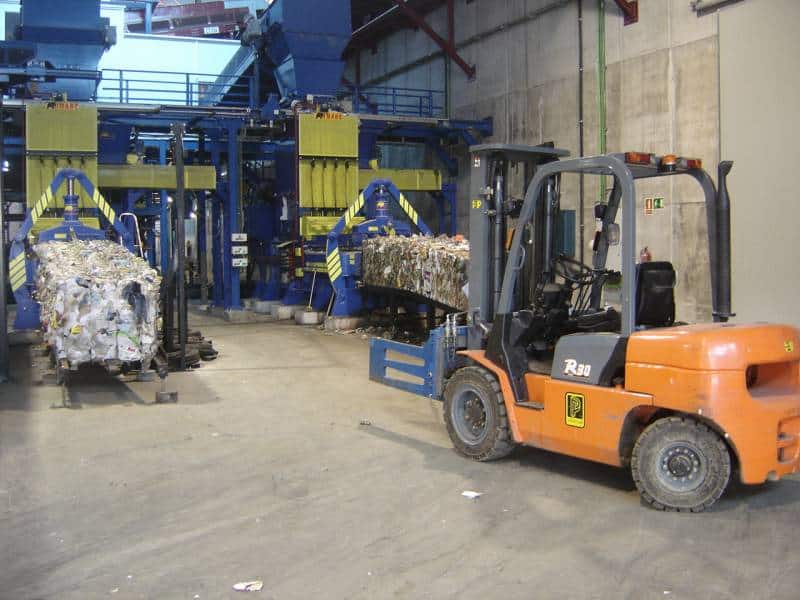
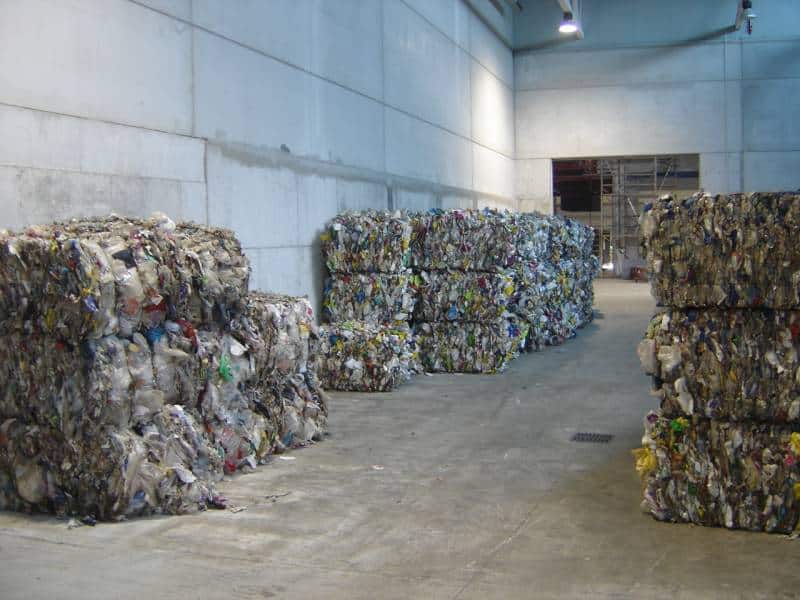
O - WAREHOUSE OF RECOVERED PRODUCTS
The automatic and manual separation process carried out in the pretreatment hall means that more than 16,000 tons/year of materials are recovered and apt to be recycled (paper/cardboard, glass, plastic, metal, tetra bricks), which are stored as compressed bales in this area to be transported to the final recuperator.
P - RECEPTION
After being weighed on the scale, the trucks go to the reception hall, where the unload pits of the MBT plant, measuring 5,650 m3, and the Waste-to-Energy plant, measuring 6,000 m3, are located. The W-T-E ones are only for waste not apt to be processed in the MBT plant.
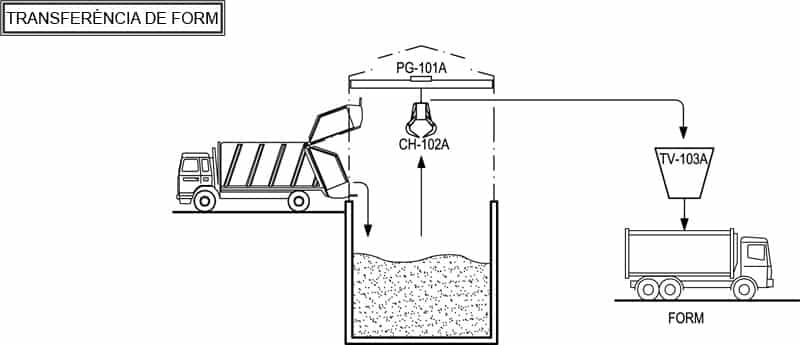
Q - BIOWASTE TRANSFER
Here, the FORM –organic matter collected separately– generated in the Maresme area arrives. This waste is unloaded and fed automatically to the containers in which the waste will travel to an external biological treatment plant –in Vallès Oriental– where energy and quality compost are obtained from it.
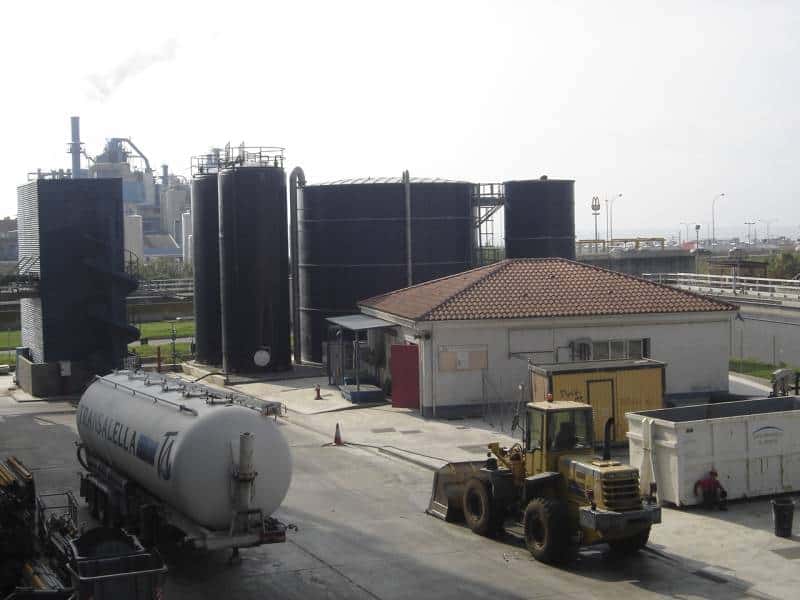

R - WASTE WATER TREATMENT
In this facility, the liquid or leachate effluents generated in the different processing areas of the MBT plant before discharging it to the sewage system are treated.
This is a first screening, followed by a complex biological treatment and double filtering –ultrafiltering plus reverse osmose–, and the process ends with the evaporation of part of the last concentration obtained.
S - WASTE-TO-ENERGY PLANT
Here, a process is followed to recover energy from the different types of waste generated in the MBT plant and other coming from outside.
Thanks to the heat generated in the combustion of the waste in the 2 furnaces-boilers, high pressure steam is obtained and it is sent to a turbine to produce electric energy.
The resulting gas of the combustion coming out from the furnaces is duly depurated in accordance with the strictest regulations before releasing them into the atmosphere. In the depuration process several reactives are used (lime, active carbon, urea, ammonia, etc.) to combine different chemical and physical processes that ensure the elimination of pollutants.
The electricity production that can be exported to the power network is close to 85 milion kWh/year, equivalent to the domestic electric consumption of 85,000 people (population formed by adding together that of Masnou, Premià de Mar, Calella and Arenys de Mar).
T - WASTE SIMULATOR
Here, we focus in a very special way to the operation of the plant through a machinery technology trip, and through the route followed by the waste in the different processes. We will turn the industrial process into a little space and sensorial adventure, thanks to a 3D film and the mobile platforms.
This is currently a test in process.
Here follow a few images from the 3D film.
Power generator
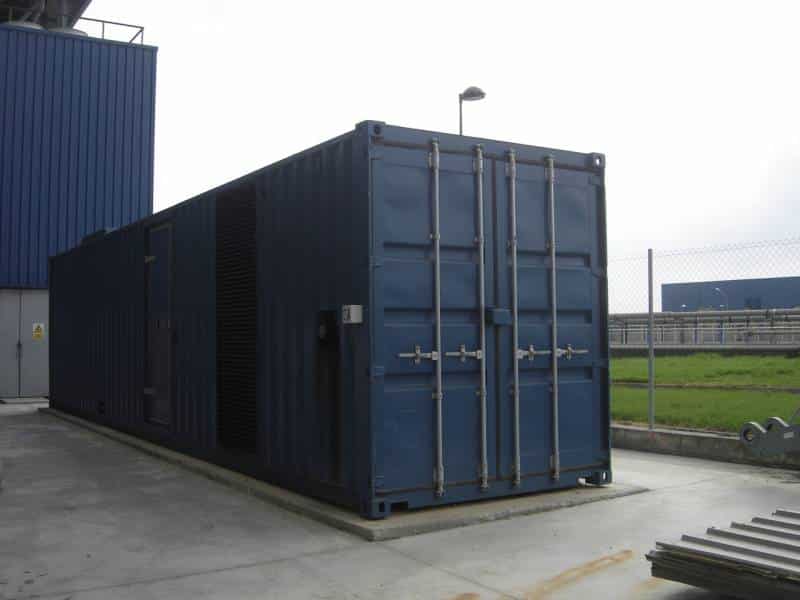

U - POWER GENERATOR
This is a device capable of producing electricity. It is very useful in case of accidental power supply cuts in order to keep the equipment of the Centre working.